While creating web pages, it may be beneficial to ensure that the height of both the outer and inner <div> elements are always identical. This guarantees a responsive configuration with a uniform appearance across various display sizes. In this article, we will explore techniques for setting the height of the outer div to be consistently equal to a specific inner div utilizing CSS and JavaScript.
Table of Contents:
Techniques to Ensure the Height of an Outer Div Matches a Specific Inner Div
You can employ CSS and JavaScript to automatically modify the height of the outer div to align with that of a specific inner <div>. This is particularly useful for maintaining consistent layouts.
Utilizing Flexbox, Grid, JavaScript, and jQuery serves this purpose well. Below, we will elaborate on these techniques:
Technique 1: Utilizing CSS Flexbox
Employ Flexbox to organize the elements within the container. This guarantees that the heights of the inner and outer divs are equivalent.
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Flexbox Equal Height</title>
<style>
.outer {
display: flex;
align-items: stretch;
border: 2px solid black;
}
.inner {
flex: 1;
background-color: lightblue;
padding: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="outer">
<div class="inner">Content here</div>
<div class="inner" id="target">This div controls the height</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Output:
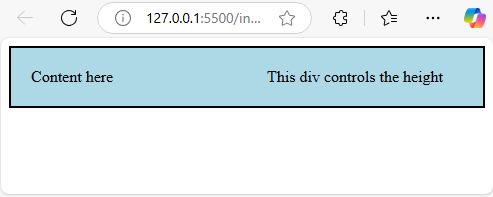
Explanation: Within this code, the display: flex property is implemented to force child elements to stretch and match the height of the tallest element. The align-items: stretch attribute ensures that all inner elements maintain the same height.
Technique 2: Using JavaScript for Height Matching
JavaScript can be utilized to ensure that the heights of the outer and inner div are in sync. This is particularly beneficial when CSS fails to achieve the desired outcome.
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Equal Height</title>
<style>
.outer {
display: flex;
align-items: stretch;
border: 2px solid black;
}
.inner {
flex: 1;
background-color: lightblue;
padding: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="outer">
<div class="inner">Content here</div>
<div class="inner" id="target">This div controls the height</div>
</div>
<script>
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function () {
function matchHeights() {
let containers = document.querySelectorAll(".inner");
let maxHeight = 0;
containers.forEach(container => {
container.style.height = "auto";
});
containers.forEach(container => {
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, container.offsetHeight);
});
containers.forEach(container => {
container.style.height = maxHeight + "px";
});
}
matchHeights();
window.addEventListener("resize", matchHeights);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
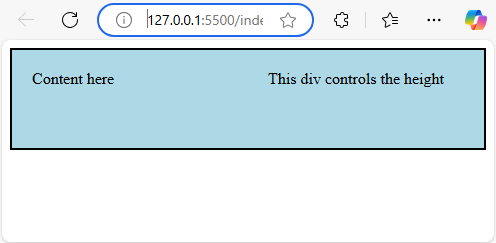
Explanation: In this snippet, the document.getElementById(‘target’).offsetHeight is utilized to align the height of the inner and outer divs. To guarantee proper functioning, window.onload can be included, while window.onresize can be used to monitor changes in window size.
Technique 3: Applying CSS Grid for Automatic Sizing
CSS grid layout can also be employed for the alignment of elements.
Example:
<style>
.outer {
display: grid;
grid-template-rows: auto;
border: 2px solid black;
}
.inner {
background-color: lightgreen;
padding: 20px;
}
</style>
<div class="outer">
<div class="inner">Some text here</div>
<div class="inner" id="target">A longer text block that determines height</div>
</div>
Output:
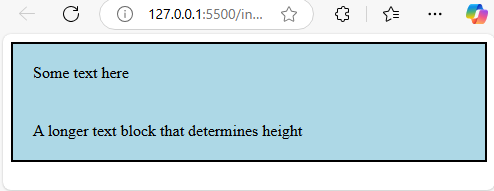
Explanation:The grid configuration is utilized to modify the height of the row. This technique is suitable if you possess several child elements and aim to maintain an orderly appearance.
Summary
The techniques mentioned above represent the most effective methods to equalize the height of both outer and inner divs. You may apply display: flex and align-items: stretch in CSS flexbox to ensure that child elements are uniform in height, or employ JavaScript to adjust the height of the outer div according to the height of the inner div. If you have numerous child elements, the CSS grid serves as a more advantageous choice. This approach guarantees a neat and adaptable layout regardless of screen size.
How to Ensure That the Height of an Outer Div Matches a Specific Inner Div? – FAQs
Aligning heights enables a responsive design that remains consistent irrespective of the inner div’s content.
Common techniques include utilizing CSS Flexbox, CSS Grid, JavaScript, or jQuery.
By setting the display to flex and aligning items to stretch, you enable the child element to adopt the height of the tallest child.
Absolutely, you can employ JavaScript to adjust the height of the outer div so that it corresponds with the inner div using offsetHeight.
Certainly, CSS Grid automatically modifies row heights contingent on the content.
The article How to Ensure That the Height of an Outer Div Matches a Specific Inner Div? was originally published on Intellipaat Blog.

